Preliminary Work
Fragment screening and HIV therapeutics
Fragment screening is reviewed, providing opportunities for discovery of novel anti-HIV drugs.
Bauman JD, Patel D & Arnold A. Top. Curr. Chem. 317 181-200 (2012)
PubMed PMID: 21972022
PubMedCentral PMCID: PMC3565459
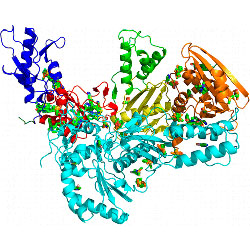
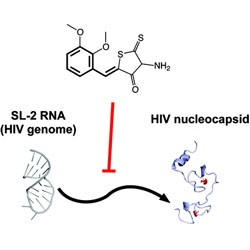
Identification of HIV-1 Inhibitors Targeting the Nucleocapsid Protein
A high-throughput assay is used to discover drugs that block the action of HIV nucleocapsid
Breuer, S., Chang, M. W., Yuan, J. and Torbett, B. E. J. Med. Chem. 55, 4968-4977 (2012).
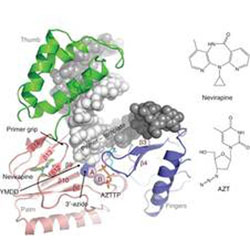
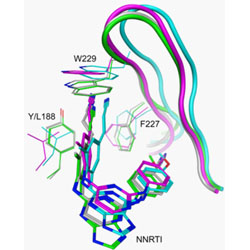
HIV-1 Reverse Transcriptase Complex with DNA and Nevirapine Reveals Non-nucleoside Inhibition Mechanism
The crystal structures of reverse transcriptase with DNA and two types of inhibitors have been solved. The RT-DNA complex in the crystal could bind either the non-nucleoside inhibitor nevirapine or the nucleoside inhibitor AST-triphosphate, but not both. The structures reveal the complementary roles these different classes of inhibitor play in widely-used anti-AIDS therapies.
K. Das, S. E. Martinez & E. Arnold (2012) Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 19, 253-259.
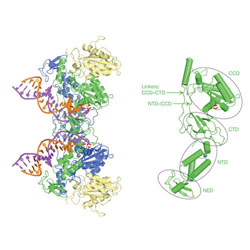
Retroviral Intasome Assembly and Inhibition of DNA Strand Transfer
The structure was solved of full-length retroviral integrase from prototype foamy virus in complex with its cognate DNA. The structure shows the organization of retroviral intasome , with an integrase tetramer tightly associated with a pair of viral DNA ends. The structure reveals the extensive protein-DNA and protein-protein interactions involved in retroviral integration, and provides a model for the HIV-1 intasome.
S. Hare, S. S. Gupta, E. Valkov, A. Engelman & P. Cherepanov (2010) Nature 464, 232-236.
A comparison of the ability of rilpivirine (TMC278) and selected analogues to inhibit clinically relevant HIV-1 reverse transcriptase mutants.
A combination of structure activity relationships and X-ray crystallography was used to examine non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors that are structurally related to rilpivirine to determine their ability to inhibit wildtype reverse transcriptase and several clinically relevant mutants.
3D Molecular Models of Whole HIV-1 Virions Generated with CellPACK
Methods for creating 3D models of mature HIV are presented.

Snapshot of the equilibrium dynamics of a drug bound to HIV-1 reverse transcriptase.
Femtosecond experiments and theory expose the molecular level dynamics of rilpivirine bound to HIV-1 RT.
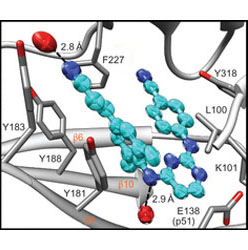
Fragment-Based Screen Against HIV Protease
Two new inhibitor binding sites were discovered on wild-type HIV protease using fragment-based screening techniques. Protease was cocrystallized or soaked with chemical fragments using five different crystal forms, and 378 data sets were collected. Fragment binding induces a new conformation and crystal form in protease with the active site inhibitor TL-3. This study is the first fragment-based crystallographic screen against HIV protease, revealing two new exosites that stabilize inhibitor binding at the active site.
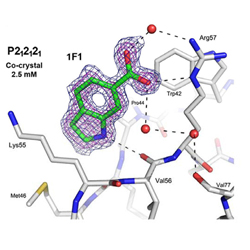
Structural and Functional Insights into Alphavirus Polyprotein Processing and Pathogenesis
The alphavirus replication machinery consists of four nonstructural proteins produced as a single polyprotein. The structure has been solved of P23 in a precleavage form. The P2/3 cleavage site is located at the base of a narrow cleft and is not readily accessible, and the nsP2 protease active site is over 40 Angstroms away, supporting a regulated, trans cleavage mechanism.

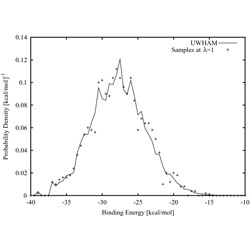
Theory of binless multi-state free energy estimation with applications to protein-ligand binding.
The paper describes a simplified technique for computing free energies and expectations from multiple ensembles.
Tan Z, Gallicchio E, Lapelosa M, Levy RM. J Chem Phys. 136(14):144102 (2012).
Small Molecule Regulation of Protein Conformation by Binding in the Flap of HIV Protease
Crystallographic structures of two small indoles reveal a binding site that favors a closed conformation of the HIV protease flaps.

